OBD2 Protocols: A Comprehensive Guide
In the dynamic world of automobiles, OBD2 protocols stand as a vital link between vehicles and diagnostic tools. These standardized protocols facilitate seamless communication with a vehicle’s onboard computer, granting access to essential information. Understanding OBD2 protocols has never been more crucial, as they enable us to diagnose issues, monitor performance, and enhance fuel efficiency.
Whether you’re a car enthusiast, mechanic, or everyday driver, this knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions, ensure safety, and potentially save on repairs. In this article, we’ll explore what the protocols are.
Let’s dive in!
What is CAN Bus Protocol?
Introduction to CAN Bus
A Controller Area Network (CAN bus) is a standardized communication system in vehicles that enables microcontrollers and devices to exchange data without the need for a central computer. It utilizes a message-based protocol and was initially developed to reduce copper wiring in automobiles. However, it has found applications in various other fields as well. In this system, data is transmitted serially in frames, and if multiple devices attempt to transmit simultaneously, the one with the highest priority takes precedence while others defer. All devices, including the transmitting one, receive these frames.
CAN Bus Applications and Time Implementation
The CAN bus has become widely used in various vehicle brands like VW, Audi, BMW, Mercedes, Ford, Mazda, Volvo, and more since 2004 (some earlier, some later). It is set to become the standard protocol of the automotive industry. By 2008, all vehicles sold in Canada and the US were required to implement the CAN bus, eliminating the uncertainty of the previous five signaling protocols.
CAN Bus Physical Configuration
The CAN bus is a simple twisted pair of wires, terminated with resistors of 120 Ohms at each end (in most cases). Only ECUs are directly connected to the CAN bus, while other components, like sensors, motors, lighting, switches, etc., are wired solely to the ECUs. Some modern vehicles also include other communication systems like MOST, LIN, Bluetooth, and FlexRay alongside the CAN system, and in some cases, both CAN and ISO/KWP2000 systems are used together.
CAN Bus Communication Protocol
In the CAN bus, the two wires, CAN-H and CAN-L, have the same voltage when idle (about 2.5V) or a voltage difference of 2V when a signal is present on the bus. Each electronic control unit has its own unique CAN identity code, acting like an address. To communicate with another control unit, an ECU needs to know the CAN identification of the recipient (although not in all cases). When a message is sent on the CAN bus, all CAN controllers “see” the message, but only the intended controller “reacts” to it.
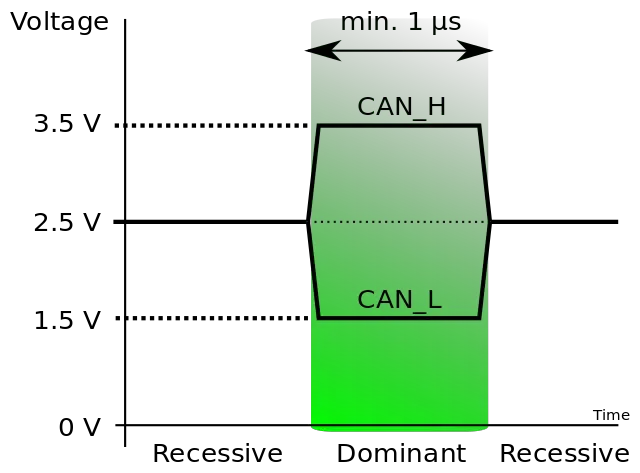
For onboard diagnostics, a vehicle using the CAN bus can only respond to an OBD-II request from a tester that is CAN bus compliant. Vehicle manufacturers must use the OBD protocol specified in ISO 15765 (Diagnostics On CAN) from model year 2008 onwards.
Checking CAN Bus Presence via OBD Socket
To check if the CAN bus is used in a vehicle and accessible via the OBD socket, one can connect a resistance meter across pin 6 and pin 14. The combined resistance of the two termination resistors (each 120 Ohms) should result in an overall resistance of 60 Ohms (refer to the vehicle specifications). This resistance measurement can help confirm the presence of the CAN bus in the vehicle’s OBD system.
Five Communication Protocols
The modern OBD-II interface utilizes five common protocols, and identifying the specific protocol in use can often be determined by examining the pins on the J1962 connector. While manufacturers can provide some clues, the most accurate method involves inspecting the DLC (Data Link Connector) with the aid of a wiring schematic to confirm the protocol being employed.
As mentioned above, if you have an old car manufactured before 2008, it’s essential for you to know the other 4 protocols besides ISO 15765.
Here are the key points for each protocol using bullet points:
ISO 9141-2
Data rate: 10.4 kBbaud.
Used in Chrysler, European, and Asian vehicles.
Pin 7: K-line, Pin 15: L-line (optional).
Communication similar to RS-232.
High voltage is Vbatt (battery voltage).
Message length limited to 12 bytes, including CRC.
ISO 14230 KWP2000
Data rate: 1.2 to 10.4 kBbaud.
Common in European and Asian vehicles.
Pin 7: K-line, Pin 15: L-line (optional).
Similar physical layer to ISO 9141-2.
Message can contain up to 255 bytes in the data field.
ISO 15765 CAN
Data rate: 250kbit/sec or 500kbit/sec.
Uses Pin 6: CAN High, Pin 14: CAN Low.
Widely used in various vehicles.
Offers fast and efficient data transmission.
SAE J1850 PWM (Ford)
Data rate: 41.6 kBbaud.
Standard for Ford Motor Company.
Pin 2: Bus-, Pin 10: Bus+.
Employs “Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Non-Destructive Arbitration” (CSMA/NDA).
Message length limited to 12 bytes, including CRC.
SAE J1850 VPW (General Motors)
Data rates: 10.4 or 41.6 kBbaud.
Standard for General Motors.
Pin 2: Bus+.
Bus idles low, high voltage is +7V.
Decision point is +3.5V.
Message length limited to 12 bytes, including CRC.
Employs CSMA/NDA.
You can detect your car’s protocol by observing the pinouts. Keep in mind that Pins 4 (battery ground) and 16 (battery positive) are present in all configurations. Additionally, ISO 9141 and ISO 14230 share the same pinout, making it impossible to differentiate between them by merely examining the connector.
Conclusion
In conclusion, OBD2 protocols play a pivotal role in our automotive experience, providing crucial data and insights. Understanding these protocols empowers drivers, mechanics, and enthusiasts to diagnose issues, improve performance, and make informed decisions. With OBD2 protocols as our gateway, we unravel the true potential of our vehicles, creating a safer and more efficient driving future.
Share this insightful article on OBD2 protocols with others who seek a deeper understanding of their vehicles. If you have any questions or thoughts, leave a comment below – let’s engage in a lively discussion about the power of OBD2 protocols!

Leave a Reply