P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
Did your car scanner throw the P0420 code? Are you confused about which decision to make and whether to keep driving?
Continue reading to briefly evaluate your current situation.
- P0420 Definition: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1).
- Code Type: Generic – P0420 indicates the same problem whether you’re having a Chevy, Honda, or Nissan, etc.
- Can I drive with the P0420 code? Yes, but doing so will further damage your catalytic converter.
- Easy to fix? Intermediate to advanced level.
- Cost: $400 – $2200 (common).
Now you know that the P0420 code may not imply immediate danger.
To avoid wasting time and money on finding the problem, let’s dive into four causes of the P0420 code and their corresponding solutions.
What Does the P0420 Code Mean?
The P0420 is the diagnostic code for a defective or underperforming catalytic converter. However, this code may pop up due to other reasons not directly related to the converter.
What Is The Catalytic Converter’s Function?
To protect the environment, the catalytic converter limits and breaks down the harmful exhaust gasses (e.g., Carbon Monoxide and Nitrogen Oxide) from internal combustion engines.
How Do You Know Your Catalyst System Is Below Efficiency?
There are two oxygen sensors sitting near the converter, one at the front (upstream) and another at the rear (downstream).
The upstream sensor measures the O2 level of exhaust fumes exiting the engine. Meanwhile, the downstream sensor checks the O2 level of gasses leaving the converter.
In normal conditions, the data from the upstream sensor will fluctuate while the downstream’s must remain steady. If both sensors output the same data, the catalyst system is inefficient, harmful gasses will be released into the environment, and P0420 is set.
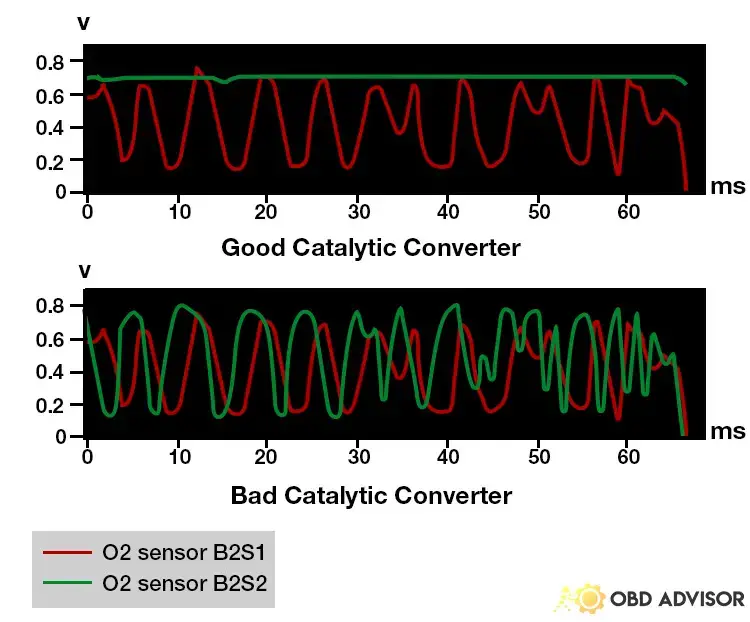
The P0420 code may not seem serious enough to stop driving. However, the catalyst system may be further damaged, and the car will fail emission tests.
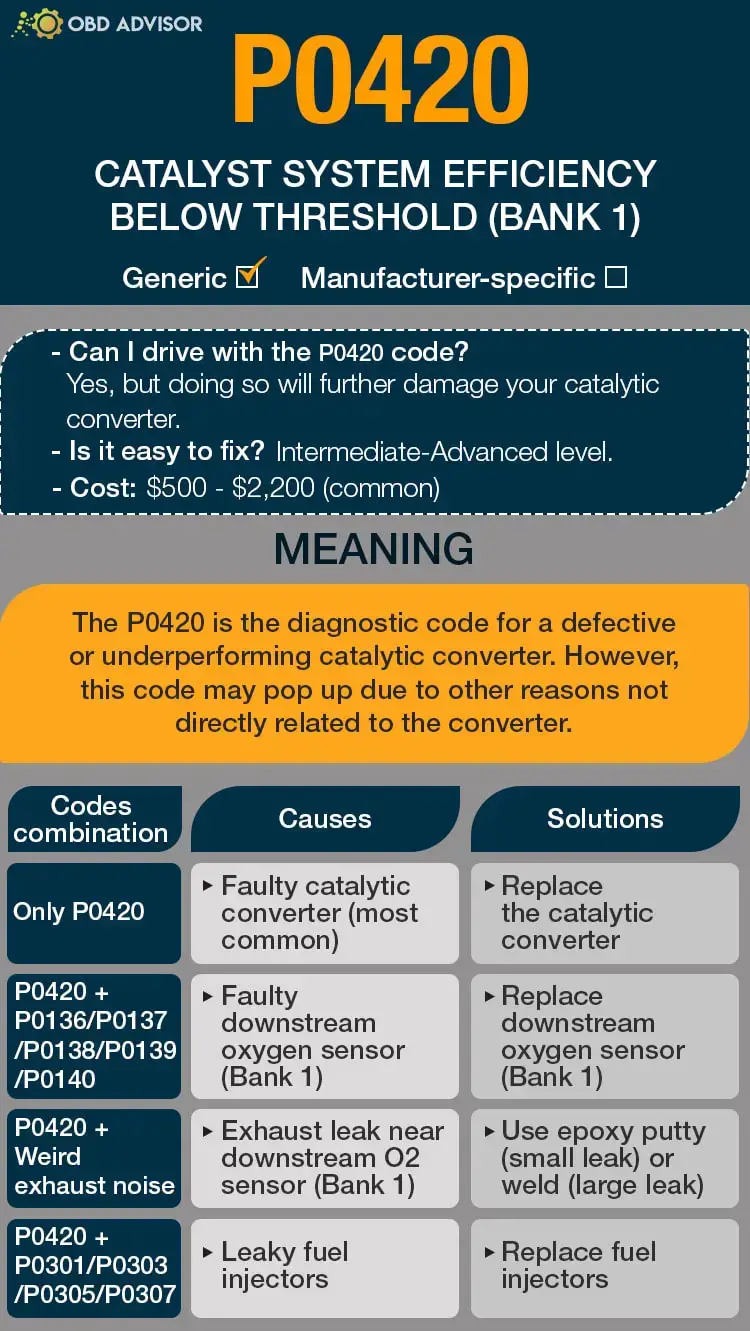
P0420 Causes Identification: Quick View
A faulty catalytic converter is often the culprit when a scanner indicates the P0420 code. However, the downstream oxygen sensor or a failing engine component may be the root cause. Hence, another code may show up with the P0420.
Below are the likely causes of this code and their possible solutions.
| Codes Combination | Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Only P0420 | Faulty catalytic converter (most common) | Replace the catalytic converter |
| P0420 + P0136/P0137/P0138/P0139/P0140 | Faulty downstream oxygen sensor (Bank 1) | Replace downstream oxygen sensor (Bank 1) |
| P0420 + Weird exhaust noise | Exhaust leak near downstream O2 sensor (Bank 1) | Use epoxy putty (small leak) or weld (large leak) |
| P0420 + P0301/P0303/P0305/P0307 | Leaky fuel injectors | Replace fuel injectors |
Note: The causes for each code combination are the most common ones. There can be some uncommon issues hidden under those codes.
P0420: Causes, Symptoms, And How to Fix
If a vehicle outputs the P0420 diagnostic code after scanning, the following might be the cause.
Cause #1: Faulty Catalytic Converter
A faulty catalytic converter is the most common cause of the P0420 code. Sometimes, this might be due to:
- Structural damage caused by thermal shocks
- Weak welding points
- Direct hits from rocks and debris
- Unburnt fuel coats the catalyst
In any case, a faulty catalytic converter fails to convert exhaust fumes to environmental-friendly gasses.
Therefore, the exhaust fumes exit from the catalytic converter without any changes (filtering or cleaning). As a result, the upstream and downstream oxygen sensors’ reading will be the same, triggering P0420.
Look out for the following symptoms to identify a fault catalytic converter.
- Check engine light
- Dark exhaust smoke
- Gasoline smell around the car
- Excess heat under the car
- Poor engine performance
The chances of restoring the catalytic converter to its initial condition are slim. A suitable replacement is the best solution though it is pricey.
Cause #2: Faulty Downstream Oxygen Sensor
The downstream oxygen sensor’s function is to keep track of the catalytic converter’s efficiency. If the sensor fails, it may tell the PCM that the catalytic converter is underperforming (in fact, it isn’t.)
There are no obvious symptoms of a faulty downstream oxygen sensor. You can conduct an O2 sensor test to determine whether it is faulty or not.
If it is your problem, your scan tool will trigger only P0420 or with other codes like P0136, P0137, P0138, P0139, and P0140.
The most realistic solution is to replace the oxygen sensor. Buying the part and changing it yourself will save you money from the repair shop.
Cause #3: Exhaust Leak Near Downstream O2 Sensor
The exhaust leak affecting the output voltage can be found near the downstream oxygen sensor.
The exhaust system can suck oxygen into the exhaust flow through a leak due to the pressure differences. Consequently, the sensors will capture incorrect readings due to the extra oxygen, causing the PCM to set P0420.
The following are the common symptoms of an exhaust leak:
- Unusual blowing noise from underneath the car
- Low engine performance
- Unpleasant odor around the car during operation
In the case of small leaks, epoxy glue will resolve the issue. However, some larger leaks may require welding.
Cause #4: Leaky Fuel Injectors
Leaky fuel injectors can also be the root cause of the P0420 code. When the fuel injector leaks, excess fuel in liquid form reaches the combustion chamber.
As a result, some amount of fuel is left unburnt and passed to the exhaust system. Over time, the waste fuel builds up and overloads the catalyst system, reducing its efficiency drastically.
The following symptoms can mean that a car has leaky fuel injectors.
- Gasoline smell in and around the car
- Rough engine performance and idling
- Increased fuel consumption
- Heavy exhaust fumes
- Excessive heat under the car
The only way to resolve the problem is to replace the leaky fuel injectors with suitable ones.
How Much Does It Cost to Fix P0420?
The cost of resolving the P0420 depends on the root cause of the problem. A fault catalytic converter is the most common cause which costs $400 – $2,000 to repair yourself. If it is too difficult to handle this job, you will pay $500 – $2200 to visit a mechanic.
The following are the possible costs of fixing the P0420.
The Estimated Repair Cost Of P0420
| Solutions | Cost |
|---|---|
| Replace the catalytic converter | DIY: $400 – $2000 Repair shop: $500 – $2200 |
| Replace downstream oxygen sensor (Bank 1) | DIY: $20 – $95 Repair shop: $100 – $450 |
| Use epoxy putty (small leak) | DIY: under $10 Repair shop: not recommended |
| Weld the leak (large leak) | DIY: not recommended Repair shop: $30 – $100 |
| Replace fuel injectors | DIY: $400 – $900 Repair shop: $600 – $1,200 |
Note: The data in this table was collected in June 2022. The actual price depends on many factors, such as your car’s make and year, mechanic’s rate, etc.
You Ask, I Answer
Once the catalytic converter fails or underperforms, the car’s computer transmits the P0420 and related diagnostic codes.
By now, you should be able to understand the likely causes of the code and decide how to fix them.
Do you have questions or comments regarding the P0420 code? Please reach out to us using the comment section.
See ya!
Read more: The 9 Best OBD2 Scanners for 2024: The Only Review You Need
