P0120 Code: Understanding TPS “A” Circuit Malfunction
If you’ve ever encountered the P0120 OBD-II trouble code, you know how frustrating it can be to have your vehicle’s check engine light illuminate. This code refers to the “Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch “A” Circuit” issue, which can cause several serious issues if not addressed.
In this article, we’ll take a comprehensive look at the P0120 code, including its severity, common symptoms, underlying causes, and the necessary diagnostic and repair steps. By understanding this information, you’ll be able to address the issue quickly and efficiently, getting your vehicle back on the road in no time.
So, let’s dive in.
P0120 Code: An Overview
Here is a summary of the P0120 code. Check it out!
- Definition: Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch “A” Circuit
- Severity: Medium
- DIY Skill Level: Intermediate
- Continue To Drive?: Yes (short-term)
- Estimated Repair Cost: $50 – $200
What Does The P0120 Code Mean?
P0120 is a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that indicates there is a problem with the throttle position sensor (TPS) circuit, specifically circuit “A.”. While it is a generic code that can occur in various car makes and models, it is particularly more common in Chevrolet, Toyota, and Nissan among others.
The TPS is part of the engine management system, which controls the air-fuel mixture and other engine parameters to optimize performance and emissions. The TPS works together with the throttle valve and the Engine Control Unit (ECU) to ensure that the engine receives the correct amount of air.
When you press the accelerator pedal, the throttle valve opens, allowing more air to enter the engine. The TPS sends a signal to the ECU indicating the position of the throttle valve. The ECU then uses this information to calculate the correct amount of fuel to inject into the engine.
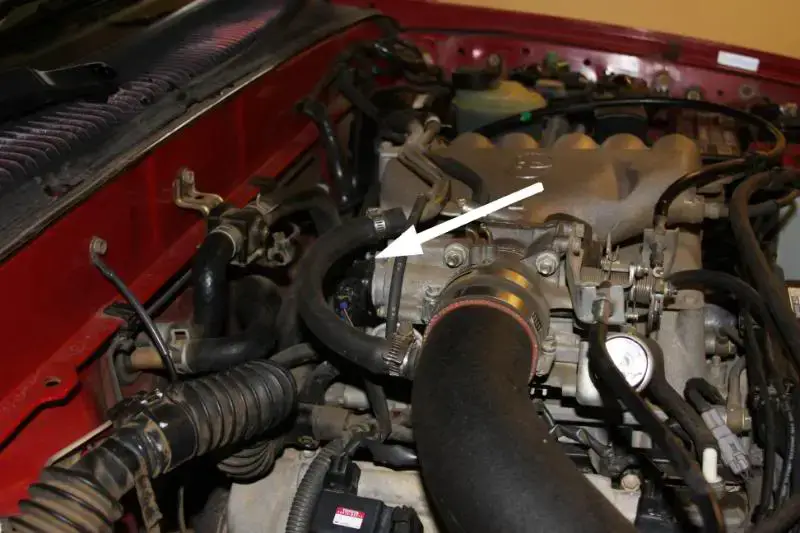

If the TPS “A” circuit is faulty, the TPS may not be able to send a signal to the ECU, or the ECU may not be able to receive the signal, triggering the code P0120. Specifically, when the ECM identifies that the voltage output from TPS circuit “A” exceeds the designated voltage range, in contrast to TPS sensor circuit “B,” the P0120 code is triggered. The specific voltage range may differ depending on the vehicle’s manufacturer and model.
Note: In some vehicle models, the ECU monitors the TPS and the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor together. The ECU expects a consistent relationship between the throttle position and the manifold pressure. If there is a significant difference between the two, it can trigger the P0120 code.
How Severe Is P0120?
The P0120 code is of medium severity. While it doesn’t indicate an immediate danger or major mechanical failure, it should be addressed promptly to prevent potential issues from getting worse.
Driving with the P0120 code in the short term is generally safe. However, if ignored for a long time, it could cause reduced fuel efficiency, drivability problems, or even damage to other engine components.
To ensure your vehicle’s longevity and optimal performance, it’s recommended to have the code diagnosed and repaired as soon as possible. Consult a qualified mechanic to identify the root cause and make the necessary repairs. Taking this proactive approach will help prevent further complications in the future.
Read more: P0122 – Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch “A” Circuit Low
What Are The Symptoms of P0120?
When your vehicle experiences the P0120 code, you may notice the following symptoms:
- Check Engine Light (CEL) illuminated on the dashboard
- Failsafe mode
- Reduced engine power or lack of response when pressing the accelerator pedal
- Irregular or fluctuating idle speed
- Poor fuel efficiency
- Hard starting
Read more: P0121 – Throttle/Pedal position sensor/switch “A” circuit
What Causes P0120?
The P0120 code can be triggered by various underlying causes, including:
- Malfunctioning TPS sensor (most common)
- Damaged or frayed wiring in the TPS circuit
- Loose or poor electrical connections
- Corrosion or debris on the sensor or connectors
- Faulty ECM or related components such as accelerator position sensor, MAP sensor.
Read more: P1516 Chevy Code: Throttle Position Sensor Issues Explained
DIY Guide To Diagnosing and Repairing P0120
In this section, we’ll provide the tools and parts you’ll need, along with a step-by-step procedure to help you diagnose and fix the P0120 code yourself. By following this guide, you can save money on repairs and better understand your vehicle’s throttle position sensor.
Essential Tools and Parts
To diagnose and repair the P0120 code, you may need the following tools and parts:
- OBD-II scanner or code reader
- Multimeter
- TPS replacement (if necessary)
- Electrical contact cleaner
- Wire connectors and electrical tape (for wiring repairs)
Step-by-step Procedure
Step 1: Retrieve Stored DTCs
Connect the OBD-II scanner or code reader to retrieve the stored trouble codes and any additional relevant data.
Step 2: Inspect Throttle Pedal
Inspect the throttle pedal position sensor and its wiring for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires or loose connections. Pay close attention to the wiring harness near the sensor.
Step 3: Check the Sensor and Connector
Check for any corrosion or debris on the sensor or its connectors. Clean them if necessary to ensure proper electrical contact.
Step 4: Test Voltage Signals
Use a multimeter to test the voltage signals from the TPS circuit and compare them to specifications provided by the manufacturer. Ensure the TPS is receiving and transmitting the correct voltage signals. If the voltage signals are outside the expected range or erratic, replace the throttle position sensor.
Step 5: Inspect Related Components
Inspect other related components, such as the accelerator position sensor, MAP sensor, and their respective wiring connections, for any signs of damage or loose connections. Repair or replace as needed.
Step 6: Clear Codes and Test Drive
Clear the trouble codes using the OBD-II scanner and test drive the vehicle to ensure the issue has been resolved.
Note: It’s recommended to consult the vehicle’s service manual or seek professional assistance for specific diagnostic and repair steps tailored to your vehicle’s make and model.
DIY Repair Level and Estimated Costs
Diagnosing the P0120 code can be moderately challenging, requiring some technical knowledge and the use of specialized tools. The level of DIY repair for this code is considered intermediate.
The estimated costs for the main repair tasks associated with the P0120 code can vary depending on factors such as the vehicle make, model, and the specific cause of the issue. Here’s a general breakdown of potential costs:
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost Range |
| Diagnostic Fee | $50 – $100 |
| Wiring Repair | $50 – $200 |
| Throttle Position Sensor Replacement | $60 – $100 (aftermarket part)$100 – $200 (OEM part) |
Remember, if you’re unsure about any step or lack the necessary tools and expertise, it’s always advisable to consult with a qualified mechanic or automotive technician to ensure proper diagnosis and repair. They can provide accurate guidance and ensure the issue is resolved effectively and safely.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the P0120 OBD-II trouble code is super important to keep your vehicle running smoothly. By knowing the signs to look out for, the possible causes, and the steps for diagnosing and fixing the issue, you’ll feel confident handling the problem and avoiding any additional headaches. Of course, it’s always a good idea to reach out to a qualified mechanic for expert advice and assistance.
If you found this information helpful, feel free to share it with fellow car enthusiasts. Don’t forget to leave a comment below sharing your experiences or questions.
Stay informed and keep your car running smoothly!
Reference Sources
AutoZone, Symptoms of a Bad Throttle Position Sensor.
Autoditex, THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS).
